[Southeast University’s News Net, August 28] (Correspondent: Shi Ran) Prof. Yao Honghong’s research team from the School of Medicine of Southeast University released the latest research achievement titled “Gut microbiota from NLRP3-deficient mice ameliorates depressive-like behaviors by regulating astrocyte dysfunction via circHIPK2” on “Microbiome” online, the renowned academic periodical in the field of microbiology.
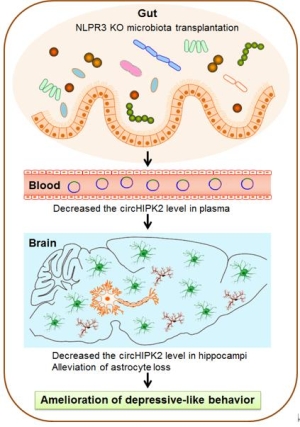
Depression is an affective disorder caused by the interaction of social, environmental and individual factors and is characterized by high morbidity, high recurrence rate, high disability rate and high suicide rate. It is ranked second in the global burden of disease. Prof. Yao Honghong's research team found that NLRP3 knockout mice showed significant behavioral differences when compared with wild-type littermates, and their gut microbiota composition changed significantly, indicating that such behavioral difference may result from the change of gut microbiota. Afterwards in order to determine the role of gut microbiota therein, the research team transplanted the gut microbiota of NLRP3 knockout mice, and then found that the gut microbiota transplantation can avoid the increase of spontaneous activity caused by knockout of NLRP3 gene; besides, it can also improve the depression-like behavior of mice induced by chronic unpredictable stress. The research team further found that the transplantation of gut microbiota can significantly ameliorate the depression-like symptoms in mice by inhibiting the expression of circular RNA-HIPK2 in the brain and regulating the brain's astrocyte dysfunction induced by chronic unpredictable stress.
The research results revealed a novel mechanism of host-microbiota interaction: the gut microbiota of transplanted NLRP3 knockout mice can regulate the astrocyte dysfunction through circular RNA-HIPK2 so as to ameliorate depressive symptoms. This study will be conducive to elucidate the interaction between gut microbiota and circular RNA and the new relationship between gut microbiota and depression, and has provided experimental evidence for the future treatment of depression and clinical application of microbial transplantation. The research work was guided by Prof. Yao Honghong with young teacher Zhang Yuan, graduate students Huang Rongrong and Cheng Mengjing as co-first authors. Relevant work has received funding support from the National Key Research and Development Program, the Excellent Youth Fund of National Natural Science Foundation of China and the General Programs, etc.
The paper was released on https://microbiomejournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s40168-019-0733-3 in “Microbiome” on August 22.
Article submitted by: the School of Medicine
(Editor-in-charge: Wu Chan, reviewed by: Li Xiaonan)
















