[Southeast University News Network, March 17] (Correspondents: Zhang Xin’ge, Sun Wei) Recently, the research team of Academician Cui Tiejun from Southeast University cooperated with Professor Qiu Chengweifrom National University of Singapore and Professor Luo Yu from Singapore Nanyang Technological University, proposed, designed and implemented a light-driven digital coding hypersurface that can program electromagnetic functions. On this light-driven digital metasurface platform, the reflected phase response of microwaves can be adjusted in real time by the intensity of visible lights, which has solved the problem of crosstalk between microwave signals and DC signals caused by the previous multi-channel electronically controlled metasurfaces that required a large number of complex physical wires for connection; meanwhile, the non-contact remote programmable control system has laid down foundation for the development of a highly integrated remote programmable hypersurface system. Relevant research results were published in “Nature Electronics” with the title of “An optically driven digital metasurface for programming electromagnetic functions”. Corresponding authors include Professor Jiang Weixiang, Professor Cui Tiejun and Professor Qiu Chengwei from the National University of Singapore, and the first author is Zhang Xin’ge, a doctoral student of Southeast University.
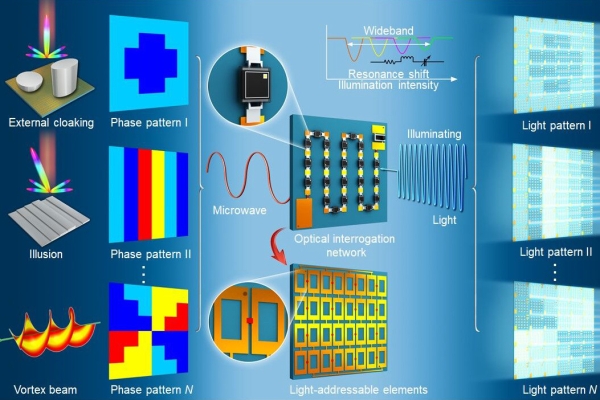
A metasurface is an artificial structure array composed of a large number of sub-wave length units arranged periodically or non-periodically on a two-dimensional plane, which can manipulate the electromagnetic waves in a flexible manner. Because of its ultra-thin structure and strong self-designability, the metasurface has been favored by a large number of researchers, in particular, the digitally coded metasurface which can complete the multifunctional programmable control of electromagnetic waves on a single platform. In the microwave band, a common method of constructing a digitally coded metasurface is to load semiconductor devices (such as PIN diodes and varactors) into the metasurface unit. However, this method generally requires a large number of wires, external power and complex control circuits to provide DC control signals to drive the metasurface. In addition, the external power supply and the controller must be connected with the super surface via a wire, which will increase the system volume and also cause crosstalk between DC and microwave signals.
Different from the wired electrical control methods, the wireless light control methods have recently been proposed and applied to the regulation of microwave dynamic metasurface (related results were published in “Advanced Science” in 2018, DOI:10.1002/advs.201801028 and “Applied Physics Letter”, DOI: 10.1063/1.5045718). However, the implemented microwave light-controlled metasurface is narrow-banded and can only be regulated in an overall or atone-dimensional direction, which greatly limits the programmability of digitally encoded metasurface. The rapid development of wireless communications and the increasingly complex electromagnetic environment have increasing demands for multi-tasking capabilities and integration of electromagnetic devices and systems. Therefore, the design and the implementation of highly integrated electromagnetic devices and systems with strong programmability have become a research hotspot, but there are still some difficulties in constructing digitally coded metasurfaces featuring high programmability, broadband, and wireless remote control in the microwave band.
In order to overcome the above difficulties, an ultra-compact wideband light-controllable programmable digital metasurface platform was designed by integrating multiple independent silicon photocell-based optical sensing networks behind a carefully designed varactor-based metasurface. The designed optical sensing network can receive visible lights of different intensities, and then generate different bias voltages, thereby regulating the microwave reflection phase of the broadband metasurface. By receiving different light patterns, different phase distributions can be generated in real time on the aperture of the light-controllable programmable digital platform, thereby achieving electromagnetic functions of different varieties. In addition, this type of light-driven programmable digital platform, as an electronic bridge, can connect optical input and microwave output, and has verified the feasibility of vector microwaves that can be controlled by scalar light intensity. It is expected to provide new technical solutions to develop advanced optoelectronic hybrid devices and the communication systems that integrate visible lights and microwave in the future.
Submitted by: the School of Information Science and Engineering
(Editor-in-charge: Sun Yan, reviewed by: Li Xiaonan)
















