[Southeast University News Network, April 7] (Correspondent: Xu Feng) Recently, the research team of Lin Chengqi and Luo Zhuojuan from the Key Laboratory of Ministry of Education on Developmental and Disease-Related Genes, School of Life Science and Technology, Southeast University, published the paper titled “ENL initiates multivalent phase separation of the Super Elongation Complex (SEC) in controlling rapid transcriptional activation” in Science Advances, the international top journal. This article clarified the research achievement on the formation and mechanism of gene-transcribed and elongated complex.
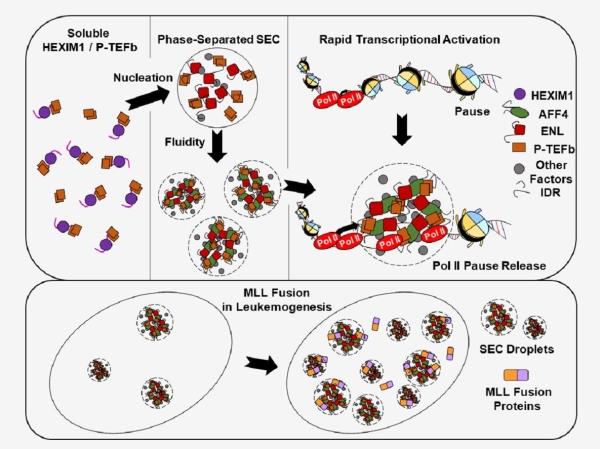
The gene transcription is the first step in the transmission of genetic information carried on DNA. The cell fate decision, the individual development, and the occurrence and development of diseases depend on differential expressions of genes. Prof. Lin Chengqi, in his previous researches, identified and found that oligomeric and macromolecular protein complexes, and super transcription extension complexes (SEC) can be released from the suspended state by phosphorylating RNA polymerase II and other factors, thus promoting effective transcription of downstream genes. However, people have been long perplexed about how the molecules outside the endomembrane system regulate the life process in an orderly manner.
The research team of Southeast University revealed that SEC-mediated multivalent phase separation would play a key role in the transcription of RNA polymerase II and its release from the suspension state, and provide a new understanding of exploring the mechanism of rapid coordinated transcriptional activation of genes from a completely new perspective. In addition, the authors also found that the transposition and fusion of SEC and MLL genes in mixed lineage leukemia (MLL) can greatly promote the separation of SEC, thereby promoting the rapid transcription of oncogenes while maintaining high expressions. This discovery will provide a new direction for exploring the SEC-related human disease pathogenesis and the drug targeting screening options.
The first author of this paper is Guo Chenghao, a PhD student in Lin Chengqi’s research team from School of Life Science and Technology of Southeast University, and Southeast University is the first corresponding institute.
Paper’s link: https://advances.sciencemag.org/content/6/14/eaay4858
Submitted by: School of Life Science and Technology
(Editor-in-charge: Hu Qiang, reviewed by: Song Xiaoyan)
















